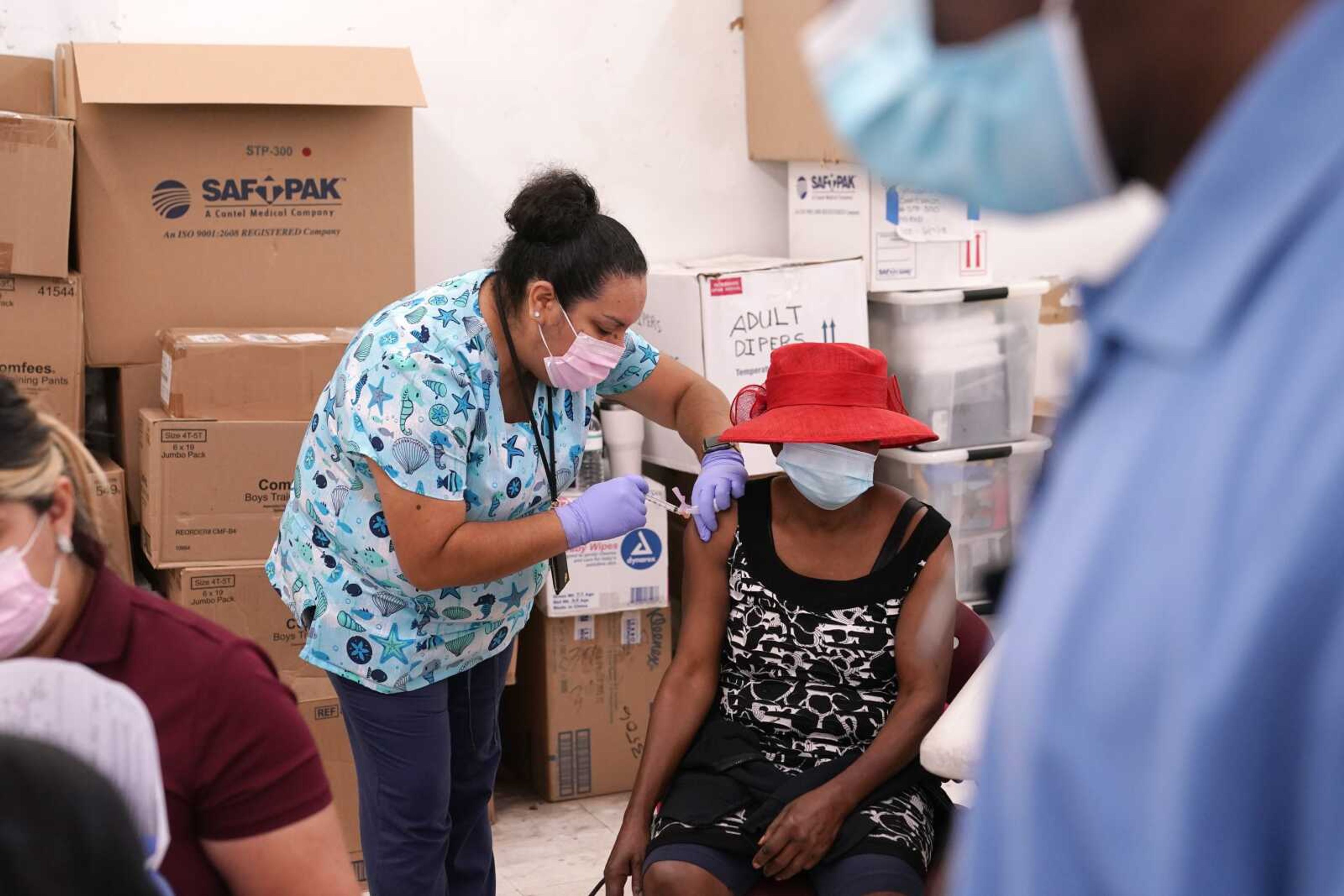
Poll: Most in U.S. who remain unvaccinated need convincing
Fewer Americans are reluctant to get a COVID-19 vaccine than just a few months ago, but questions about side effects and how the shots were tested still hold some back, according to a new poll highlighting the challenges at a pivotal moment in the U.S. vaccination campaign...
Fewer Americans are reluctant to get a COVID-19 vaccine than just a few months ago, but questions about side effects and how the shots were tested still hold some back, according to a new poll highlighting the challenges at a pivotal moment in the U.S. vaccination campaign.
Just 11% of people who remain unvaccinated say they definitely will get the shot, while 34% say they definitely won't, according to the poll by The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research.
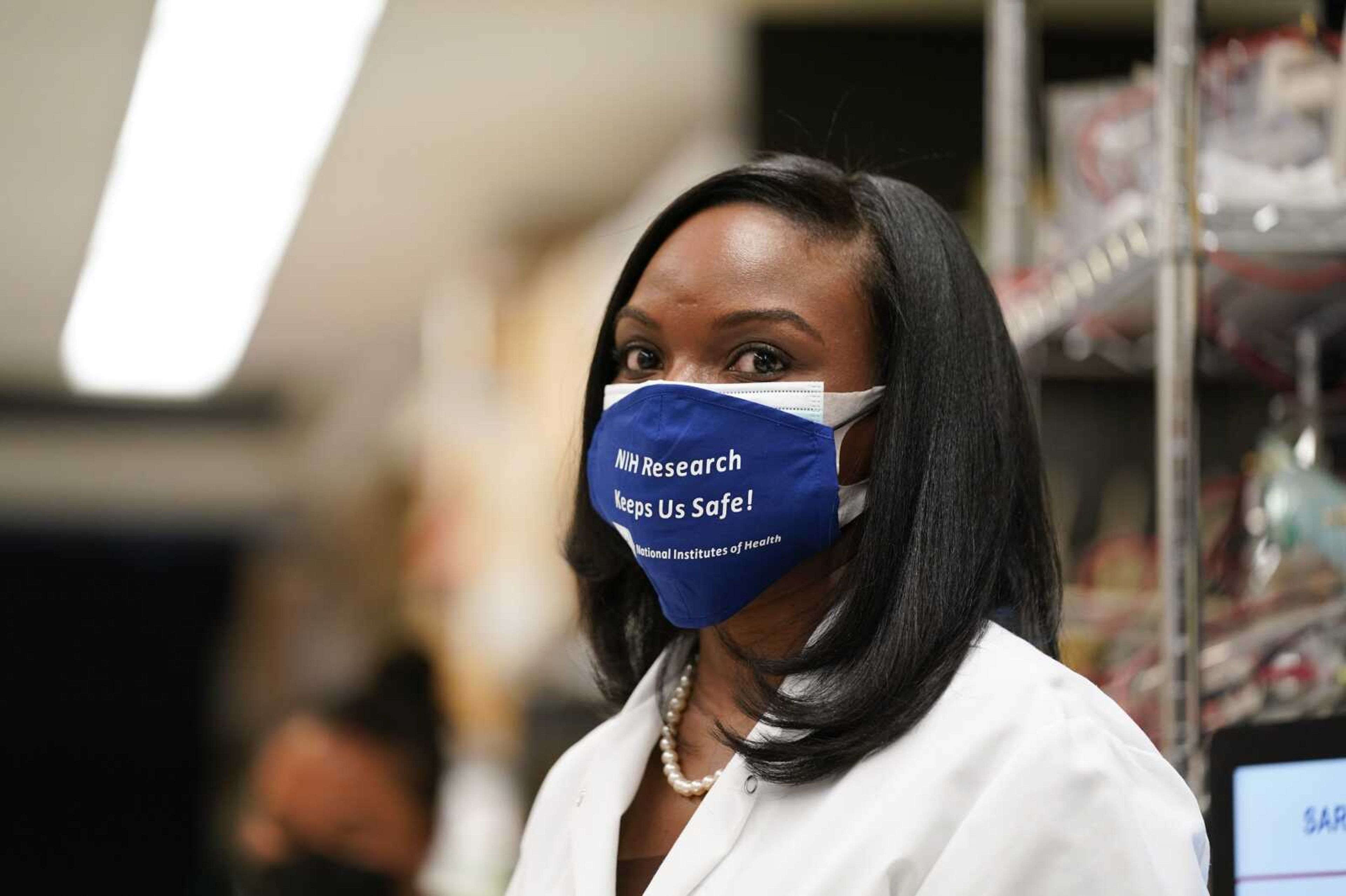
That leaves a large swath of Americans in the middle who might still roll up their sleeves -- including 27% who say they probably will and 27% who say they probably won't -- if someone credible addressed their concerns. That's where National Institutes of Health immunologist Kizzmekia Corbett comes in.
Corbett helped lead development of the Moderna shot, and she spends hours giving plain-spoken answers to questions from Americans -- especially Black Americans like her -- to counter misinformation about the three vaccines used in the U.S.
No, COVID-19 vaccines won't cause infertility: "Whoever started that rumor, shame on you."

No, the shots' speedy development doesn't mean corners were cut: "We worked our butts off for the last six years" hunting vaccines for earlier cousins of COVID-19 -- a head start that made the difference, Corbett recently told the AP.
Getting as many people vaccinated as fast as possible is critical to returning the country to normal. More than 150 million people -- about 58% of all adults -- have received at least one dose, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
As that number grows, reluctance is inching down. Overall, the AP-NORC poll found about 1 in 5 American adults say they probably or definitely won't get vaccinated, compared to about a third in January, when the shots were just rolling out.
Black Americans likewise are becoming more open to the shots, with 26% now saying they definitely or probably won't get vaccinated compared with 41% in January. That's similar to the 22% of Hispanic Americans and white Americans the poll found unlikely to get vaccinated. Among Asian Americans, just 9% say they definitely or probably won't get the shots.
Holdouts are from all over American society -- fueling experts' advice there is no one-size-fits-all vaccine message and people need to hear from trusted sources, whether that's scientists such as Corbett or their own doctors. Adults younger than 45, rural Americans and Republicans are especially likely to say they will avoid vaccination, the poll found. But again, attitudes are changing: 32% of Republicans now say they probably or definitely won't get vaccinated, down from 44% in January.
About three-fourths of those who say they are unlikely to get vaccinated have little to no confidence the vaccines were properly tested, and 55% are very concerned about side effects, the poll found. Even among those who say they will probably get vaccinated but have not done so, concerns about proper testing are elevated compared with people who have received their shots already.
In forums hosted by colleges, Black pastors, doctors and even basketball great Kareem Abdul-Jabbar, Corbett said the best way to overcome distrust is to put the science in understandable terms for strangers just like she does for family. Later this spring, she's moving from the NIH to Harvard's School of Public Health to continue both her vaccine research and that outreach to communities.
The vaccines' speedy development "is historic and it is brag-worthy," said Corbett, whose NIH team was able to customize a shot that matched the new virus after spending six years developing vaccines against other dangerous coronaviruses such as MERS.
But "really, we should have started the conversations very early about what went into it," she said, so the public understood no steps were skipped.
A combination of huge studies and real-world data show the main side effects of the U.S. vaccines are temporary fevers or aches as the immune system revs up. The shots are undergoing unprecedented safety monitoring, which last month led to a temporary pause in Johnson & Johnson vaccinations to determine how to handle an incredibly rare risk of blood clots.
Even after that pause, overall confidence in the vaccines is up slightly compared with a few months ago, with 45% of all adults now very or extremely confident that the shots were properly tested for safety and effectiveness, compared with 39% in an AP-NORC poll in February.
But side effect myths persist. Corbett calls the fertility concern "completely absurd," and in forum after forum explains why it's biologically impossible for the vaccines to alter anyone's DNA.
The repetition is OK: "People need to hear things multiple times," she said.
Plus, many Americans have some of the same questions scientists are still trying to answer, such as whether or when people might need a booster dose.
"Those are things that even I can't even answer. But what I can say is that we're doing everything we can to make sure we can answer it as soon as possible," Corbett said.
The AP-NORC poll of 1,842 adults was conducted April 29-May 3 using a sample drawn from NORC's probability-based AmeriSpeak Panel, which is designed to be representative of the U.S. population. The margin of sampling error for all respondents is plus or minus 3.2 percentage points.
Connect with the Southeast Missourian Newsroom:
For corrections to this story or other insights for the editor, click here. To submit a letter to the editor, click here. To learn about the Southeast Missourian’s AI Policy, click here.