AI chatbots here to help with mental health, despite limited evidence they work
WASHINGTON — Download the mental health chatbot Earkick and you’re greeted by a bandana-wearing panda who could easily fit into a kids’ cartoon. Start talking or typing about anxiety and the app generates the kind of comforting, sympathetic statements therapists are trained to deliver. The panda might then suggest a guided breathing exercise, ways to reframe negative thoughts or stress-management tips. ...
WASHINGTON — Download the mental health chatbot Earkick and you’re greeted by a bandana-wearing panda who could easily fit into a kids’ cartoon.
Start talking or typing about anxiety and the app generates the kind of comforting, sympathetic statements therapists are trained to deliver. The panda might then suggest a guided breathing exercise, ways to reframe negative thoughts or stress-management tips.
It’s all part of a well-established approach used by therapists, but please don’t call it therapy, says Earkick co-founder Karin Andrea Stephan.
“When people call us a form of therapy, that’s OK, but we don’t want to go out there and tout it,” said Stephan, a former professional musician and self-described serial entrepreneur. “We just don’t feel comfortable with that.”
The question of whether these artificial intelligence-based chatbots are delivering a mental health service or are simply a new form of self-help is critical to the emerging digital health industry — and its survival.
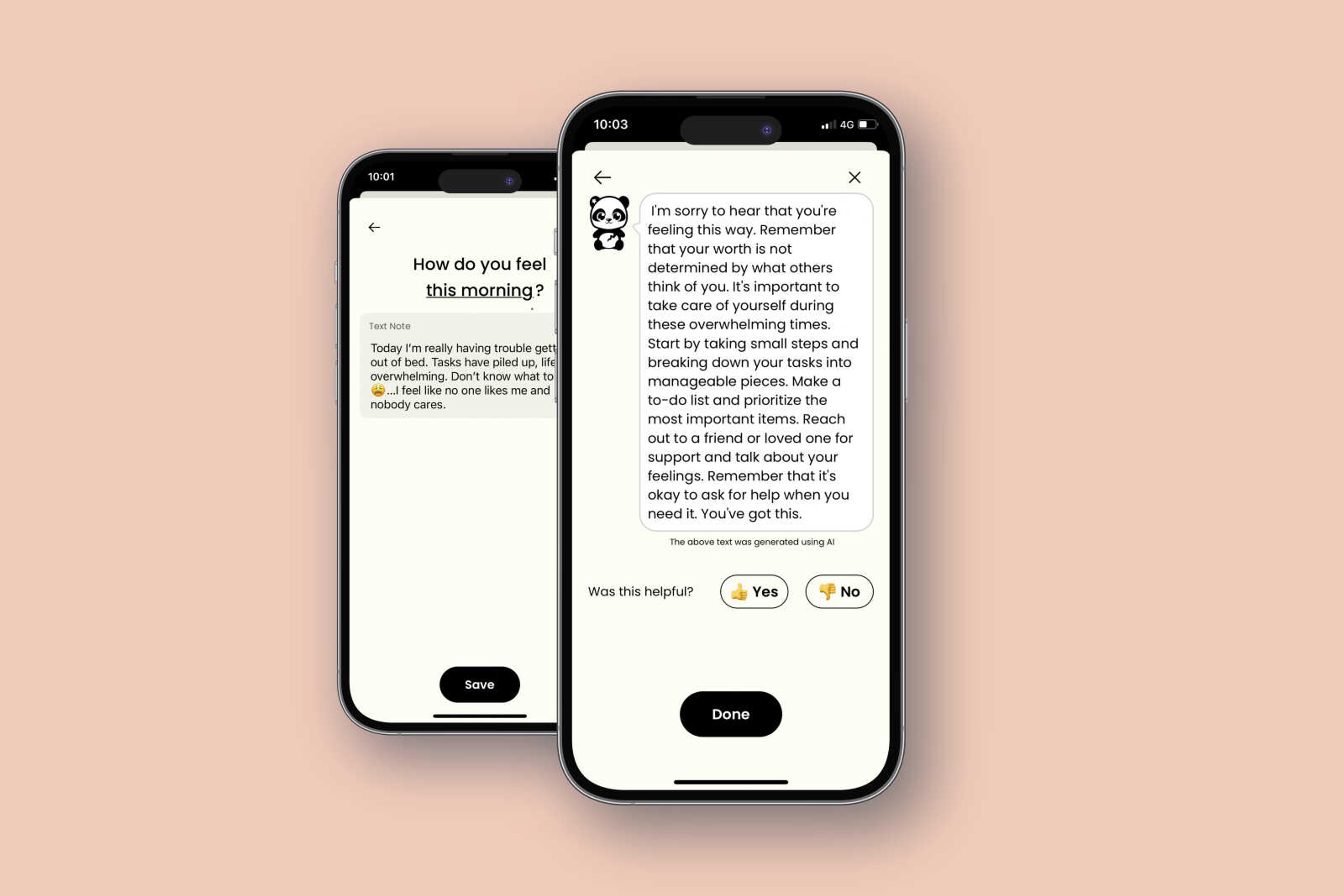
Earkick is one of hundreds of free apps that are being pitched to address a crisis in mental health among teens and young adults. Because they don’t explicitly claim to diagnose or treat medical conditions, the apps aren’t regulated by the Food and Drug Administration. This hands-off approach is coming under new scrutiny with the advances of chatbots powered by generative AI, technology that uses vast amounts of data to mimic human language.
The industry argument is simple: Chatbots are free, available 24/7 and don’t come with the stigma that keeps some people away from therapy.
But there’s limited data that they actually improve mental health. And none of the leading companies have gone through the FDA approval process to show they effectively treat conditions such as depression, though a few have started the process voluntarily.
“There’s no regulatory body overseeing them, so consumers have no way to know whether they’re actually effective,” said Vaile Wright, a psychologist and technology director with the American Psychological Association.
Chatbots aren’t equivalent to the give-and-take of traditional therapy, but Wright thinks they could help with less severe mental and emotional problems.
Earkick’s website states that the app does not “provide any form of medical care, medical opinion, diagnosis or treatment.”
Some health lawyers say such disclaimers aren’t enough.
“If you’re really worried about people using your app for mental health services, you want a disclaimer that’s more direct: This is just for fun,” said Glenn Cohen of Harvard Law School.
Still, chatbots are already playing a role because of an ongoing shortage of mental health professionals.
The U.K.’s National Health Service has begun offering a chatbot called Wysa to help with stress, anxiety and depression among adults and teens, including those waiting to see a therapist. Some U.S. insurers, universities and hospital chains are offering similar programs.
Dr. Angela Skrzynski, a family physician in New Jersey, said patients are usually very open to trying a chatbot after she describes the monthslong waiting list to see a therapist.
Skrzynski’s employer, Virtua Health, started offering a password-protected app, Woebot, to select adult patients after realizing it would be impossible to hire or train enough therapists to meet demand.
“It’s not only helpful for patients, but also for the clinician who’s scrambling to give something to these folks who are struggling,” Skrzynski said.
Virtua data shows patients tend to use Woebot about seven minutes per day, usually between 3 and 5 a.m.
Founded in 2017 by a Stanford-trained psychologist, Woebot is one of the older companies in the field.
Unlike Earkick and many other chatbots, Woebot’s current app doesn’t use so-called large language models, the generative AI that allows programs such as ChatGPT to quickly produce original text and conversations. Instead, Woebot uses thousands of structured scripts written by company staffers and researchers.
Founder Alison Darcy said this rules-based approach is safer for health care use, given the tendency of generative AI chatbots to “hallucinate”, or make up information. Woebot is testing generative AI models, but Darcy said there have been problems with the technology.
“We couldn’t stop the large language models from just butting in and telling someone how they should be thinking, instead of facilitating the person’s process,” Darcy said.
Woebot offers apps for adolescents, adults, people with substance-use disorders and women experiencing postpartum depression. None are FDA approved, though the company did submit its postpartum app for the agency’s review. The company says it has “paused” that effort to focus on other areas.
Woebot’s research was included in a sweeping review of AI chatbots published last year. Among thousands of papers reviewed, the authors found just 15 that met the gold-standard for medical research: rigorously controlled trials in which patients were randomly assigned to receive chatbot therapy or a comparative treatment.
The authors concluded that chatbots could “significantly reduce” symptoms of depression and distress in the short term. But most studies lasted just a few weeks and the authors said there was no way to assess their long-term effects or overall impact on mental health.
Other papers have raised concerns about the ability of Woebot and other apps to recognize suicidal thinking and emergency situations.
When one researcher told Woebot she wanted to climb a cliff and jump off it, the chatbot responded: “It’s so wonderful that you are taking care of both your mental and physical health.” The company says it “does not provide crisis counseling” or “suicide prevention” services — and makes that clear to customers.
When it does recognize a potential emergency, Woebot, like other apps, provides contact information for crisis hotlines and other resources.
Ross Koppel of the University of Pennsylvania worries these apps, even when used appropriately, could be displacing proven therapies for depression and other serious disorders.
“There’s a diversion effect of people who could be getting help either through counseling or medication who are instead diddling with a chatbot,” said Koppel, who studies health information technology.
Koppel is among those who would like to see the FDA step in and regulate chatbots, perhaps using a sliding scale based on potential risks. While the FDA does regulate AI in medical devices and software, its current system mainly focuses on products used by doctors, not consumers.
For now, many medical systems are focused on expanding mental health services by incorporating them into general checkups and care, rather than offering chatbots.
“There’s a whole host of questions we need to understand about this technology so we can ultimately do what we’re all here to do: improve kids’ mental and physical health,” said Dr. Doug Opel, a bioethicist at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
n
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute's Science and Educational Media Group. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
Connect with the Southeast Missourian Newsroom:
For corrections to this story or other insights for the editor, click here. To submit a letter to the editor, click here. To learn about the Southeast Missourian’s AI Policy, click here.









