Consumer behavior aggressively tracked this season
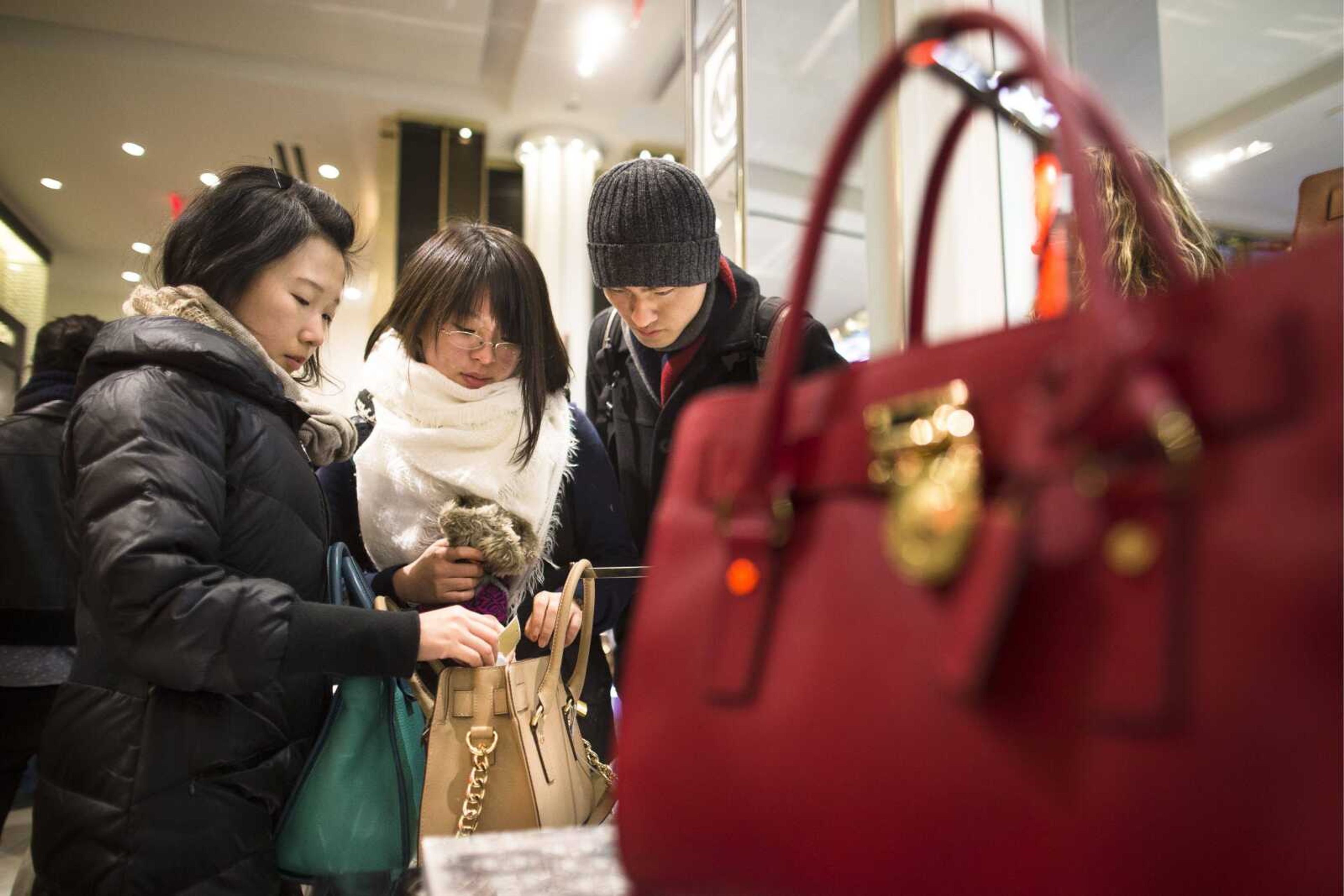
WASHINGTON -- It's a big question for marketers: What kind of a buyer are you? And, as important, what are you willing to pay? In the search for answers this shopping season, consumer behavior online and off is being tracked aggressively with help from advances in technology...
WASHINGTON -- It's a big question for marketers: What kind of a buyer are you? And, as important, what are you willing to pay?
In the search for answers this shopping season, consumer behavior online and off is being tracked aggressively with help from advances in technology.
And it can happen whether buyers are on their work computers, mobile devices or just standing in the grocery aisle. The data can be connected with other personal information like income, ZIP code and when a person's car insurance expires.
Retailers say these techniques help customize shopping experiences and can lead to good deals for shoppers. Consumer advocates say aggressive tracking and profiling also opens the door to price discrimination, with companies charging someone more online or denying them entirely based on their home price or how often they visit a site.
"You can't have Christmas any more without big data and marketers," said Jeff Chester, executive director at the Center for Digital Democracy. "You know that song where Santa knows when you've been sleeping? He knows when you're awake? Believe me, that's where he's getting his information from."
Consumer tracking has long been a part of American consumerism. Retailers push shoppers to sign up for loyalty cards, register purchased items for warranty programs and note ZIP codes to feed their mailing lists. Online stores and advertising services employ browser "cookies," the tiny bits of software code that can track a person's movements across the Internet, to analyze shoppers and present them with relevant pop-up ads.
Technology at hand
More recently, marketers have developed increasingly sophisticated ways to combine offline and online data that creates detailed profiles of shoppers. They also are perfecting location-tracking technology as a means of attracting new customers and influencing shoppers as they wander through brick-and-mortar stores.
A major push encourages shoppers to agree to be tracked in exchange for a good deal. Brick-and-mortar stores used to balk at customers who used smartphones to compare prices at rival stores, but retailers like Target are now pushing their own mobile apps and offering in-store Wi-Fi. The mobile apps entice shoppers with coupon deals or ads as they move throughout a store, while in-store Wi-Fi is another way to track a consumer's online movements.
To further lure buyers, major holiday retailers, including Macy's, Best Buy and JCPenney, have partnered with the Shopkick mobile app. If shoppers turn on the app while in their store, they can be rewarded with discounts or song downloads for trying on clothes, scanning barcodes and making purchases.
Another app, Snapette, blends American's addiction to social media sites with location technology. Aimed at women keen on fashion, consumers can see what accessories or shoes are creating a buzz in their particular neighborhood, while stores get a chance to entice nearby shoppers with ads or coupons.
Behind the scenes
Not all new technology tracking is voluntary. Stores have been experimenting with heat sensors and monitoring cellphone signals in their stores to see which aisles attract the most attention. One product called "Shopperception" uses the same motion-detection technology in the Xbox Kinect to track a customer's movement, including whether they picked up a product only to return it to the shelf. In addition to analyzing customer behavior, it can trigger nearby digital signs offering coupons and steering shoppers to certain products.
The company contends that the technology is less intrusive than other tracking devices, including security cameras, because a person's image is never stored and their movements only registered as a data point.
Marketers also are learning to overcome limitations with software cookies. One tech startup called Drawbridge claims to have found a way to link a person's laptop and mobile device by analyzing their movements online, enabling advertisers to reach the same consumer whether they're on their work computer or smartphone.
Making sense of it all
But how all that information is used and where it ends up is still unclear. The Federal Trade Commission, along with several lawmakers, has been investigating the "data broker" industry, companies that collect and sell information on individuals by pooling online habits with other information like court records, property taxes, even income. The congressional Government Accountability Office concluded in November that existing laws have fallen behind the pace of technological advancements in the industry, which enables companies to aggregate large amounts of data without a person's knowledge or ability to correct errors.
"There are lots of potential uses of information that are not revealed to consumers," said Susan Grant, director of consumer protection at the Consumer Federation of America. To protect themselves, "consumers still need to do quite a bit of shopping to make sure that they get (what) meets their needs the best and is the best price."
------
Follow Anne Flaherty on Twitter: https://twitter.com/AnneKFlaherty
Connect with the Southeast Missourian Newsroom:
For corrections to this story or other insights for the editor, click here. To submit a letter to the editor, click here. To learn about the Southeast Missourian’s AI Policy, click here.