A Listening ear
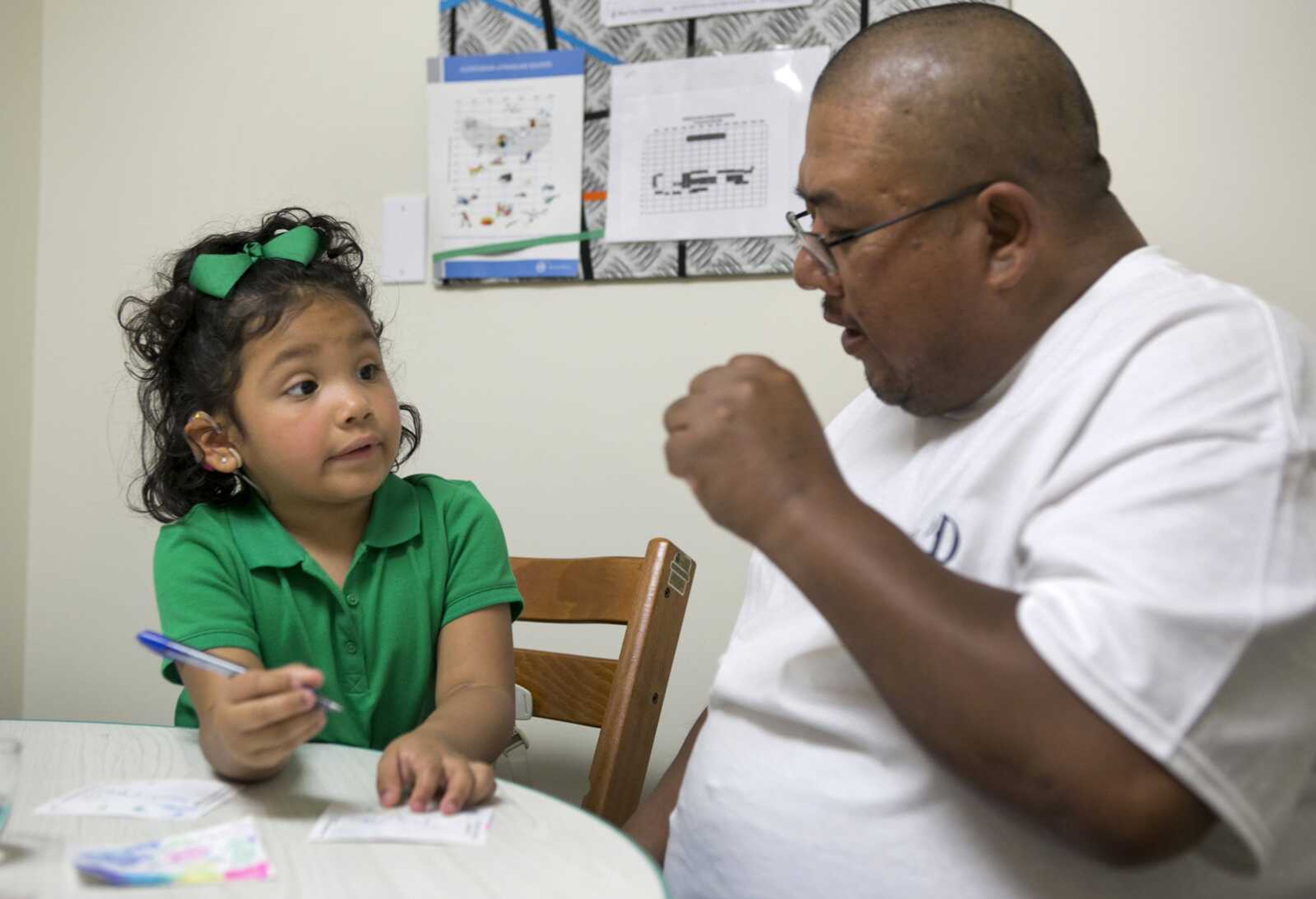
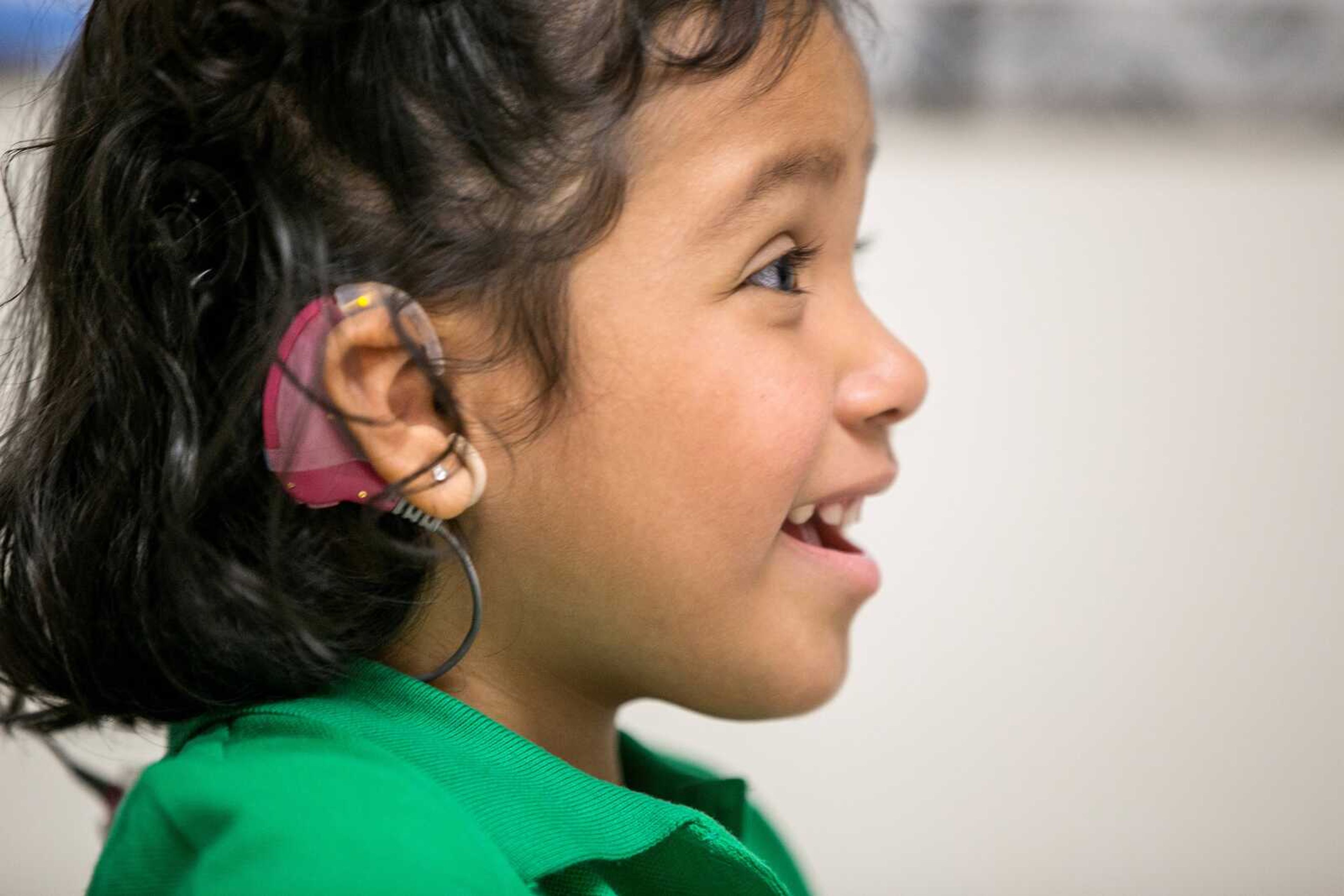
WASHINGTON -- At age 3, Angelica Lopez is helping to break a sound barrier for deaf children. Born without working auditory nerves, she can detect sounds for the first time -- and start to mimic them -- after undergoing brain surgery to implant a device that bypasses missing wiring in her inner ears...
WASHINGTON -- At age 3, Angelica Lopez is helping to break a sound barrier for deaf children.
Born without working auditory nerves, she can detect sounds for the first time -- and start to mimic them -- after undergoing brain surgery to implant a device that bypasses missing wiring in her inner ears.
Angelica is one of a small number of U.S. children who are testing what's called an auditory brainstem implant, or ABI. The device goes beyond cochlear implants that have brought hearing to many deaf children but that don't work for tots who lack their hearing nerve.
When the ABI is first turned on, "she isn't going to be hearing like a 3-year-old. She'll be hearing like a newborn," audiologist Laurie Eisenberg of the University of Southern California tells parents.
She outlined the research Friday at a meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science.

The children don't magically understand and use those sounds. "It's going to take a lot of work," Eisenberg cautioned.
Angelica cried when her ABI first was switched on, scared by the sounds.
But five months later, her mother says the youngster uses sign language to identify some sounds -- that was a cough, that's a dog barking. And she's beginning to babble like hearing babies do, as therapists work to teach her oral speech.
"It's just so awesome to hear her little voice," said Julie Lopez of Big Spring, Texas, who enrolled her daughter in the study at USC, where researchers say she's progressing well.
Many children born deaf benefit from cochlear implants, electrodes that send impulses to the auditory nerve, where they're relayed to the brain and recognized as sound. But the small fraction born without a working hearing nerve can't make that brain connection.
The ABI attempts to fill that gap by delivering electrical stimulation directly to the neurons on the brainstem the nerve normally would have targeted.
Here's how it works: The person wears a microphone on the ear to detect sound, and a processor changes it to electrical signals.
Those are beamed to a stimulator under the skin, which sends the signals snaking through a wire to electrodes surgically placed on the brain stem.
The Food and Drug Administration approved the device in 2000 specifically for adults and teenagers whose hearing nerves had been destroyed by surgery for a rare type of tumor. It doesn't restore normal hearing, but can help to varying degrees.
Then about a decade ago, an Italian surgeon started trying the ABI in deaf children, whose younger brains are more flexible and might better adapt to this artificial way of delivering sound.
Now, spurred by some successes abroad, the first U.S. studies in young children are under way at a handful of hospitals. Hearing specialists are watching the work closely.
Connect with the Southeast Missourian Newsroom:
For corrections to this story or other insights for the editor, click here. To submit a letter to the editor, click here. To learn about the Southeast Missourian’s AI Policy, click here.